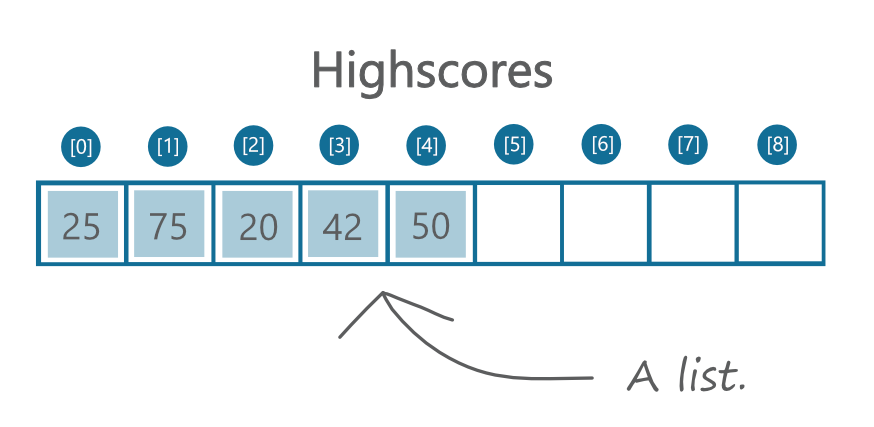
List
List is a basic data structure that stores multiple data in an ordered manner.
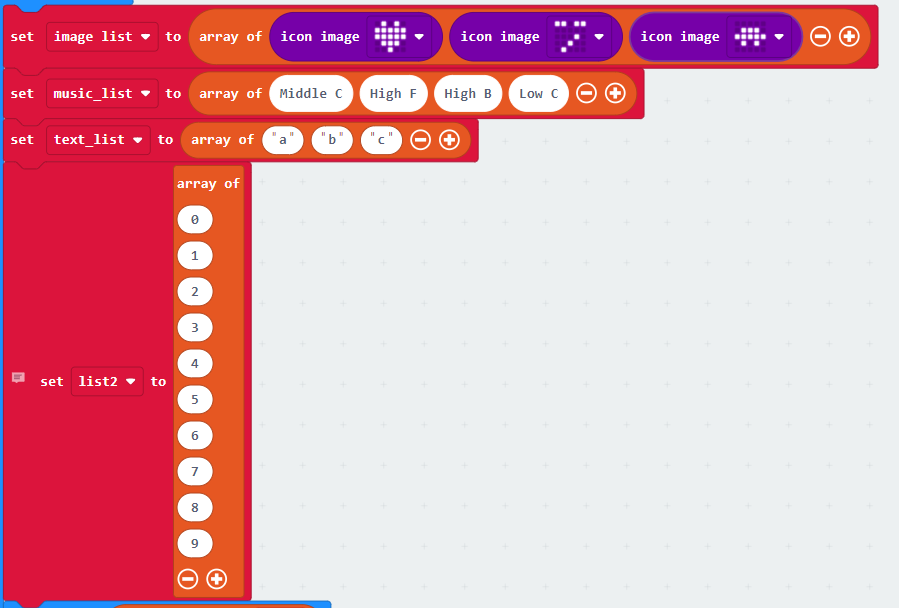
A list can store not just numbers, but also text. In MakeCode, image, sound, are all represented by test and number. Therefore we can also have a list of LED icons, or sounds.
Defining a list
Here is an example of defining a list with different data type in MakeCode Block:
To define a list in Python is extremely easy:
# Define a list named list_a with a series of number
list_a = [23, 42, 1, 0, 45, 8]
# Define a list named list_txt with some text
list_txt = ['hello', 'I', 'am', 'Jenny']
Accessing content in a list
How to read from a list? We need to use index. Index is like an address allowing you to specify which element you want to read from the list. Be careful that index starts from 0.
-
In MakeCode Block, MakeCode provide some blocks for us to read and modify the list.

Note that some reading action also delete the element from the list, such as the
get and removeblocks. -
In Python, we use
my_list[index]to access element in a list like thislist_a[4] #output would be 45 list_txt[0] #output would be helloIn Python, we also have read and remove action.
list_a.pop() # Read and remove the last element from a list list_a.shift() # Read and remove the first element from a list.Modifying a list
If we want to modify content of a list, just use = operator to assign a new value to specific element.
list_a[3]=136
Adding to and removing from a list
MakeCode block provides lots of block for adding, modifying and deleting element from a list. Most of them are easy to understand. We will look at a few common Python methods stead.
- Append (or Push): Adding to the end of a list. This is probably the most common method for adding to a list.
list_a.append(100) # add 100 to the end of list_a - Unshift: Adding to the beginning of a list.
list_a.unshift(199) # add 199 to the beginning of list_a - Delete specific element from a list.
list_a.removeAt(index)
Looping through a list
There are two ways to loop through a list.
-
Accessing each element of a list in sequence
We cannot modify the element using this method.
for element in list_a: print(element) -
Accessing by index
Using this method, we can modify content of a list. For example, let’s multiply each element by 2
for i in range(len(list_a)): list_a[i] = list_a[i]*2 print(list_a[i])