IOT
We will use our soil moisture monitor project and extended it so that we can read data remotely through bluetooth (or radio).
- What you need:
- Bitty Blue app (available on Google Play store and Apple Store)
- Alternatively, Serial Bluetooth Terminal app (available on Google Play store)
- Microbit
- A PC running MakeCode using a web browser
How does sensor data reach internet?
Sensor data usually go through a few layer of communication to reach the internet.
- A microbit acting as an end node collecting and communicating data
- A gateway receiving data from end node, package the data, and send them to internet
- Other users on the other end of internet receive data through software tools.
Communication between Machines
Today, it is essential for machine to send and receive data between each other. Just like human taking to each other, we have to have a common language and gramma. Machine talks to each other following a set of pre-defined rules. We call these rules communication protocols. Depending on the setting, different protocols are used. For example,
- UART protocol. Usually also called serial communication. This might be the most common communication protocols used between two machine connected by wire, and sometimes wireless. Our microbit talk to our computer following this protocol.
- TCP/IP. This is the protocols used for communication through internet between server and clients (for example, your browser)
Microbit support UART and Bluetooth UART. We will use these blocks in today’s project.
Wireless Communication
Let’s have a quick overview about the physics of wireless communication, and how to build simple code to send messages through radio in MakeCode. Don’t be overwhelmed if you don’t understand the physics. Most people learn these physics in senior high school or in university. Knowing electromagnetic waves are invisible energy that can carries information around is good enough.
Bluetooth
The wireless feature in Microbit can be configured as either radio, or bluetooth, but not both.
- Radio communication is very trivia to setup, and resource efficient.
- Bluetooth communication requires more advanced programming for complicated tasks, and demands for more resources.
To allow everyone to have some hands on experience on wireless without multiple microbits, we will build our project using Bluetooth. Bluetooth allows the microbit to communicate with any other devices that also has bluetooth. The Bluetooth technology we have on Microbit is Bluetooth LE. LE stands for low energy. While working with bluetooth, if you see a sad face with number 020, that means the microbit cannot run the code due to lack of resources. Try reducing your code.
Our Task
- Add Bluetooth extension
- You will notice that when you add Bluetooth, Radio is removed automatically.
Bluetooth Services
Microbit has some built-in feature to send and receive information through bluetooth. These are refered to as Bluetooth Services.

Let’s add UART service.
Pair with phone
Demo: How to pair microbit
To pair a microbit with your phone,
- hold down the Microbit button A+B+Reset, then release Reset only. You will see LEDs start filling up the screen, and a Bluetooth icon appears. That puts the Microbit in paring mode
- On your phone, open settings –> Bluetooth, and scan for bluetooth device. You should see Microbit show up.
- Click the microbit to pair with your phone.
- You may or maynot need to enter a paring code. The code is displayed on the microbit.
- After pairing success, you will see a tick on the LED screen.
Paring allowing your phone to recgonize the microbit, and allows apps on the phone to talk to it.
Connect to Microbit
From the Bitty Blue app, you should see the paired microbit listed. Tap the microbit name on the list, then you are connected.
It would be helpful if we ask the microbit to show connection status. Let’s use the on bluetooth connected and on bluetooth disconnected to display a character.
There are a number of events under the Bluetooth module. First let’s add some indicator on the Microbit to indicate when another device is connected to it via bluetooth.
Download the code, and connect to microbit it to test it out
Send UART messages
Let’s test out sending messages via UART service.
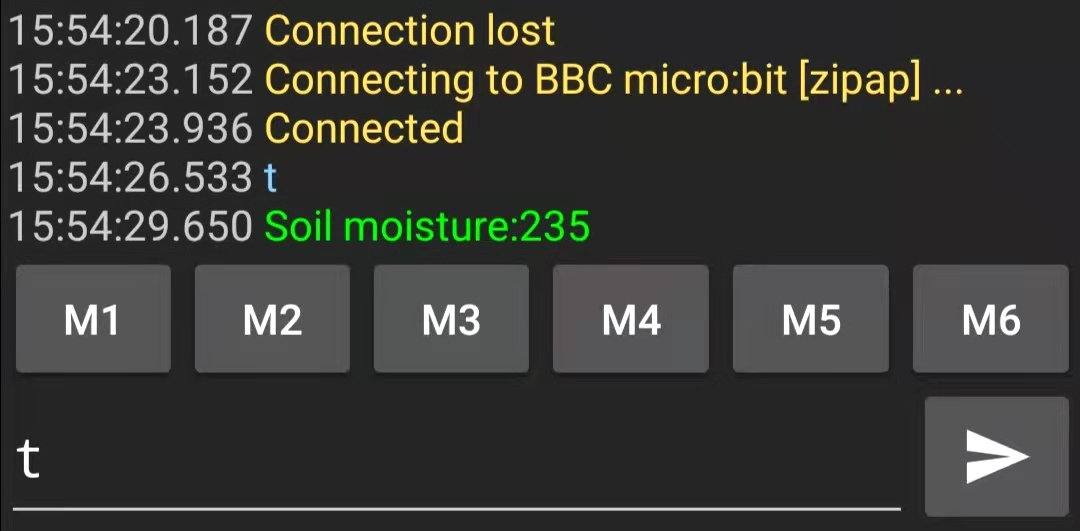
Download the code, and reconnect to microbit, and open the Message Display feature in Bitty Blue. Try pressing Button A, and watch for message popup on your phone.
Now if sending fixed message is working, let’s send our soil moisture data instead.
Now, whenever we press button A, a new measurement will be sent to our phone.
You might wonder, but I still need to press button on the microbit to see data. That doesn’t let us checking our soil’s water level from remote. Here is the last step.
Get microbit to repond whenever receiving a new UART message
To achieve true remote reading, we need to ask the Microbit to send us data when we don’t physically touch it. We can do that by sending a message to the Microbit through Bluetooth UART, and program the Microbit to reply back with the newest measurement.
This event handler function is activated whenever the Microbit receive a message through Bluetooth UART. It then write back the new measurement.
To test this feature, we need the Serial Bluetooth Terminal app. This app is good for general purpose UART communication via Bluetooth. Unfortunately it is only available for Android.
Project Link
- Bluetooth:
- Radio: