Morse Code
Morse code is a method used in telecommunication to encode text characters as standardized sequences of two different signal durations, called dots(.) and dashes(-) or dits and dahs.
Here is the sound of Morse code being sent through telegraph.
If you are curious, here is a interesting documentory about the innovation of telegraph.
Although with the new telecom technology, Morse Code has retired. It is still fun and easy and useful to learn. You’ll find people using Morse code to communicate over long distance and secretly, like using flash light to send visual Morse code at night or on sea, or using sound or numbers to send secret messages to each other.
We will build a Microbit project to send messages through Morse Code between two Microbits. We will use the following knowledge in creating this project:
- Microbit radio
- Morse code decode and encode
- Programming concept: list, function, loop, if…else…
How does Morse Code work?
First let’s understand how Morse encoding and decoding works:

This is a look up table to translate letter to Morse Code and back. Think of it as a dictionary that allows you to look up letter from code, or code from letter.
- Encode: translate a message to code
- Decode: translate from code back to message
A Microbit Morse Code Messenger
Design
- Messages will be input, and transmitted in Morse code form.
- The receiving Microbit decode the Morse code and display messages on LED screen
-
Input rule: Each code segment (letter) must be seperated by a space “ “
- User Interface:
- Button A for ‘.’
- Button B for ‘-‘
- Button A+B for space
- Shake to send
- Radio Interface:
- Radio group 1
- On shake: send morse code message, and reset ‘code_to_send’ variable
- On radio receive messages: decode the message and display on LED screen
- Internal variables:
- morse (a list) that stores Morse Code pattern from A to Z
- character (a list) that stores Alphabet A to Z
- code_to_send (string): used to store ‘.’ and ‘-‘ and ‘ ‘ input by user
- received_msg (string): used to store decoded messages
- A decoder function:
- Define a function to perform decoding
The decoder function
This is the brain of program that decode Morse code to letters. Let’s walk through and see how it works.
First of all, the message sent must follow the rule: Each letter must follow a space. Our decoder use this space to break the “.” and “-“ into segment to look up for letter. For example,
- A for “.”
- B for “-“
- A+B for “ “
| Message | Code to send | Button Press |
|---|---|---|
| “A” | ”.- “ | A, B, A+B |
| “HI” | “…. .. “ | A,A,A,A,A+B,A,A,A+B |
| “SOS” | “… — … “ | A,A,A,A+B,B,B,B,A+B,A,A,A,A+B |
We will use the SOS as an example to explain how a program decode the Morse code:
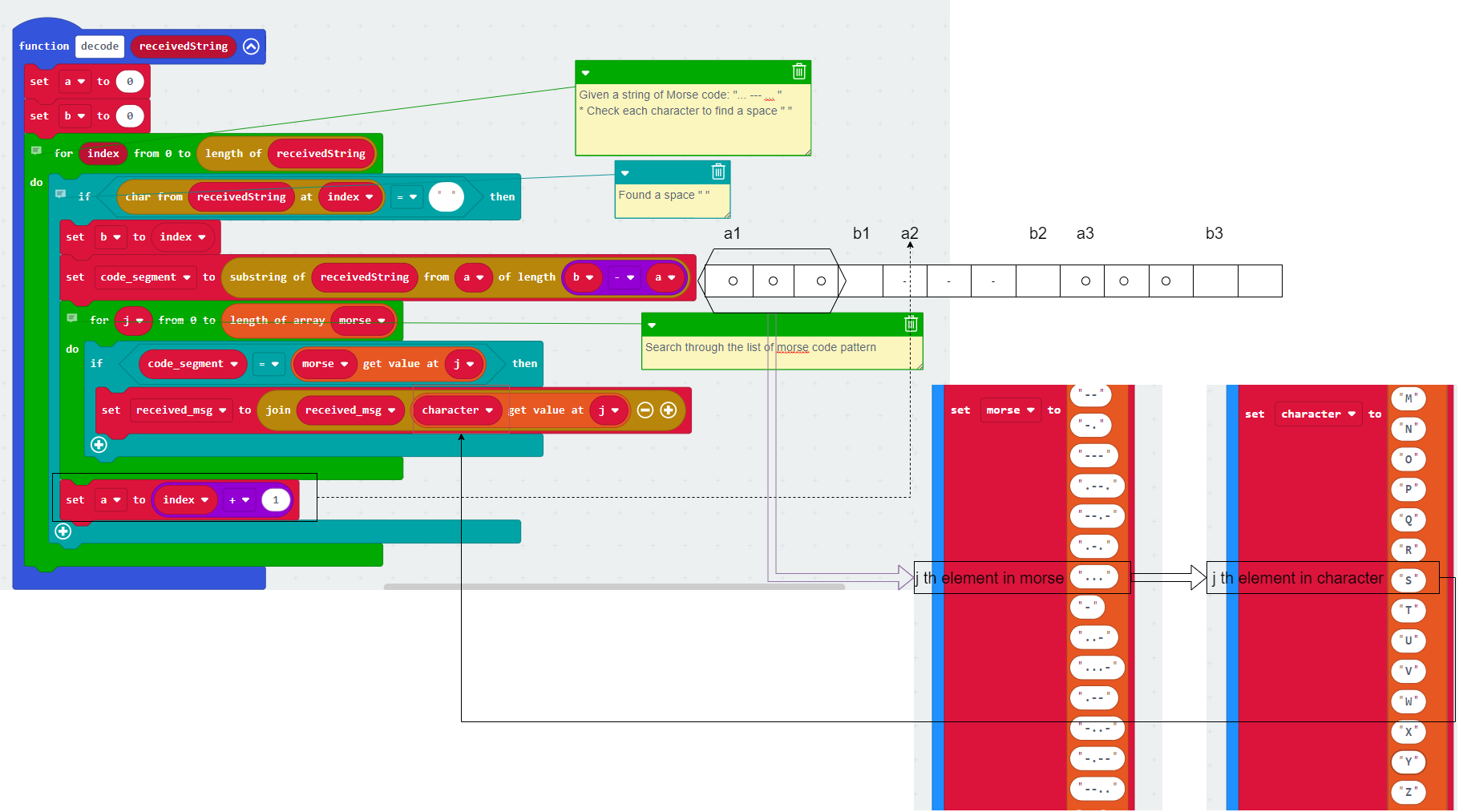
- Python code for the decode function is given below.
def decode(receivedString:str):
msg=""
a=0
b=0
for i in range(len(receivedString)):
if receivedString[i] == " ":
b=i
for j in range(len(morse)):
if morse[j]==receivedString[a:b]:
msg = msg + character[j]
a=i+1
return msg
Python Program
- Python starter project: